[ad_1]
Dynamic tables are incessantly utilized in internet packages to constitute knowledge in a structured structure. Sorting and filtering the dataset can accelerate processes when running with huge units of information. On this educational, we’ll check out the right way to create a sortable and filterable desk part in React.
You’ll to find the overall supply code in a single piece hosted on GitHub. The result is pictured under.
Must haves
Sooner than we start, this educational assumes you may have a elementary wisdom of HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React. Whilst we move over the venture step-by-step, we received’t provide an explanation for core ideas in React or JavaScript array strategies intimately. We’ll additionally use TypeScript, however the similar may also be accomplished with out it. With that being stated, let’s leap into coding.
Atmosphere Up The Undertaking
For this venture, we’ll use Vite, a powerful and standard frontend software. If you happen to don’t have already got an present React software, you’ll be able to bootstrap a brand new venture in Vite the use of one of the most following instructions within your terminal:
npm create vite@newest folder-identify -- --template react-ts
yarn create vite folder-identify --template react-ts
pnpm create vite folder-identify --template react-ts
bunx create-vite folder-identify --template react-ts
When you’re able, arrange a brand new folder for the Desk part inside the React venture with the next construction:
src
├─ parts
│ ├─ Desk
│ │ ├─ index.ts
│ │ ├─ desk.css
│ │ ├─ Desk.tsx
├─ App.tsx
index.ts. We’ll use this report to re-exportDesk.tsxto simplify import paths.desk.css. Accommodates kinds related to the part. For this educational, we’ll use vanilla CSS.Desk.tsx. The part itself.
Open Desk.tsx and export the next, in order that we will test the part so much once we import it:
import './desk.css'
export const Desk = () => {
go back (
<h1>Desk part</h1>
)
}
Within index.ts, re-export the part the use of the next line:
export * from './Desk'
Now that we’ve got the part recordsdata arrange, let’s test that it so much by way of uploading it into our app. On this educational, we’ll use the App part. In case you have an present React venture, you’ll be able to import it into your required location. Import the Desk part into your app like so:
import { Desk } from './parts/Desk'
const App = () => {
go back (
<Desk />
)
}
export default App
Producing the mock knowledge
In fact, to paintings at the desk, we’ll want some mock knowledge first. For this educational, we will use JSON Generator, a unfastened carrier for producing random JSON knowledge. We’ll use the next schema to generate the information:
[
'{{repeat(10)}}',
{
id: '{{index()}}',
name: '{{firstName()}} {{surname()}}',
company: '{{company().toUpperCase()}}',
active: '{{bool()}}',
country: '{{country()}}'
}
]
JSON Generator comes with quite a lot of integrated functionalities to generate several types of knowledge. The above schema will create an array of items with ten random items within the type of:
{
identity: 0,
identify: 'Jaime Wallace',
corporate: 'UBERLUX',
energetic: false,
nation: 'Peru'
}
Generate an inventory of entries the use of the schema above, then create a brand new report throughout the src folder known as knowledge.ts and export the array within the following approach:
export const knowledge = [
{
id: 0,
name: 'Jaime Wallace',
company: 'UBERLUX',
active: false,
country: 'Peru'
},
{ ... },
]
Open App.tsx, and cross this knowledge to the Desk part as a prop known as rows. We’ll generate the desk in accordance with this knowledge:
import { Desk } from './parts/Desk'
+ import { knowledge } from './knowledge'
const App = () => {
go back (
- <Desk />
+ <Desk rows={knowledge} />
)
}
export default App
Developing the Element
Now that we’ve got each the part and information arrange, we will get started running at the desk. To dynamically generate the desk in accordance with the handed knowledge, change the whole lot within the Desk part with the next traces of code:
import { useState } from 'react'
import './desk.css'
export const Desk = ({ rows }) => {
const [sortedRows, setRows] = useState(rows)
go back (
<desk>
<thead>
<tr>
{Object.keys(rows[0]).map((access, index) => (
<th key={index}>{access}</th>
))}
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{sortedRows.map((row, index) => (
<tr key={index}>
{Object.values(row).map((access, columnIndex) => (
<td key={columnIndex}>{access}</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</desk>
)
}
This may occasionally dynamically generate each the desk headings and cells in accordance with the rows prop. Let’s damage down the way it works. As we’re going to type and clear out the rows, we wish to retailer it in a state the use of the useState hook. The prop is handed because the preliminary worth to the hook.
To show the desk headings, we will use Object.keys at the first access within the array, which can go back the keys of the article as an inventory of strings:
const rows = [
{
id: 0,
name: 'Jaime Wallace'
},
{ ... }
]
Object.keys(rows[0]) -> ['id', 'name']
['id', 'name'].map((access, index) => (...))
To show the desk cells, we wish to use Object.values on every row, which returns the worth of every key in an object, versus Object.keys. Intimately, that is how we show desk cells:
const sortedRows = [
{
id: 0,
name: 'Jaime Wallace'
},
{ ... }
]
{sortedRows.map((row, index) => (<tr key={index}>...</tr>))}
Object.values(row) -> [0, 'Jaime Wallace']
This method makes it extraordinarily versatile to make use of any form of knowledge with our Desk part, with no need to rewrite the common sense. Thus far, we’ll have the next desk created the use of our part. On the other hand, there are some problems with the formatting.
Formatting desk cells
At the moment, the energetic column isn’t displayed. It is because the values for the ones fields are Boolean, and so they aren’t published as strings in JSX. To get to the bottom of this factor, we will introduce a brand new serve as for formatting entries in accordance with their values. Upload the next to the Desk part and wrap access into the serve as within the JSX:
const formatEntry = (access: string | quantity | boolean) => {
if (typeof access === 'boolean') {
go back access ? '✅' : '❌'
}
go back access
}
go back (
<desk>
<thead>...</thead>
<tbody>
{sortedRows.map((row, index) => (
<tr key={index}>
{Object.values(row).map((access, columnIndex) => (
<td key={columnIndex}>{formatEntry(access)}</td>
))}
</tr>
))}
</tbody>
</desk>
)
The formatEntry serve as expects an access, which in our case may also be both string, quantity, or boolean, after which returns a formatted worth if the typeof access is a boolean, which means for true values, we’ll show a inexperienced checkmark, and for false values, we’ll show a purple pass. The use of a an identical method, we will additionally structure the desk headings. Let’s lead them to capitalized with the next serve as:
export const capitalize = (
str: string
) => str?.change(/bw/g, substr => substr.toUpperCase())
This serve as makes use of a regex to grasp the primary letter from every phrase and switch it into uppercase. To make use of this serve as, we will create a utils.ts report on the root of the src folder, export this serve as, then import it into our Desk part to make use of within the following approach:
import { capitalize } from '../../utils'
export const Desk = ({ rows }) => {
...
go back (
<desk>
<thead>
<tr>
{Object.keys(rows[0]).map((access, index) => (
<th key={index}>{capitalize(access)}</th>
))}
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>...</tbody>
</desk>
)
}
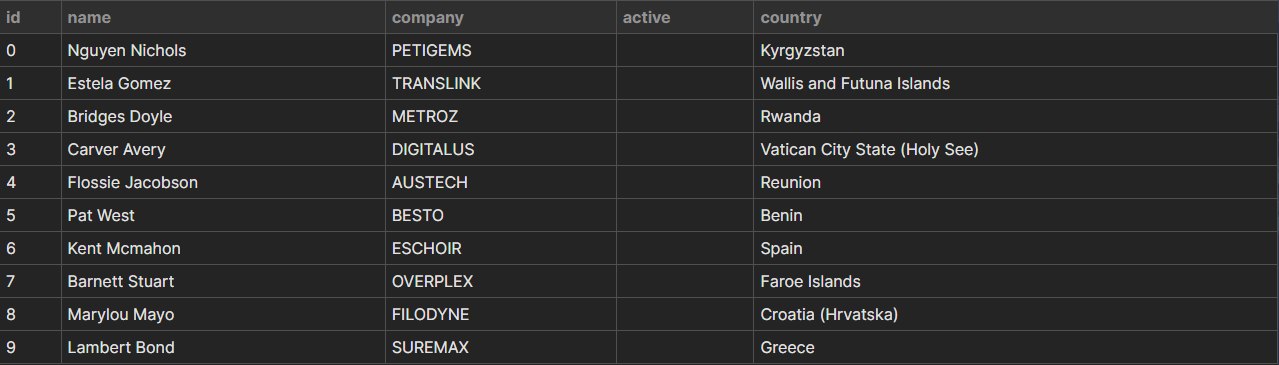
In keeping with those changes, we’ve a dynamically constructed, formatted desk.
Typing props
Sooner than we leap into styling the desk after which including controls, let’s correctly kind the rows prop. For this, we will create a sorts.ts report on the root of the src folder and export customized sorts that may be reused during the venture. Create the report and export the next kind:
export kind Information = {
identity: quantity
identify: string
corporate: string
energetic: boolean
nation: string
}[]
To kind the rows prop within the Desk part, merely import this kind and cross it to the part within the following approach:
import { Information } from '../../sorts'
export kind TableProps = {
rows: Information
}
export const Desk = ({ rows }: TableProps) => { ... }
Styling the Desk
To taste all the desk part, we’ll simplest want a few regulations. First, we need to set the colours and borders, which we will do the use of the next kinds:
desk {
width: 100%;
border-collapse: cave in;
}
thead {
text-align: left;
colour: #939393;
background: #2f2f2f;
}
th,td {
padding: 4px 6px;
border: 1px forged #505050;
}
Upload the above to desk.css. You’ll want to set border-collapse to cave in at the <desk> to steer clear of double borders. Because the desk spans all the display, let’s additionally make some changes and take away the left and correct border, as they aren’t visual anyway:
th:first-child,
td:first-child {
border-left: 0;
}
th:last-child,
th:last-child {
border-right: 0;
}
This may occasionally do away with the borders on every facet of the <desk>, leading to a cleaner glance. Finally, let’s upload a hover impact to the desk rows to help customers visually when looking out the desk:
tr:hover {
background: #2f2f2f;
}
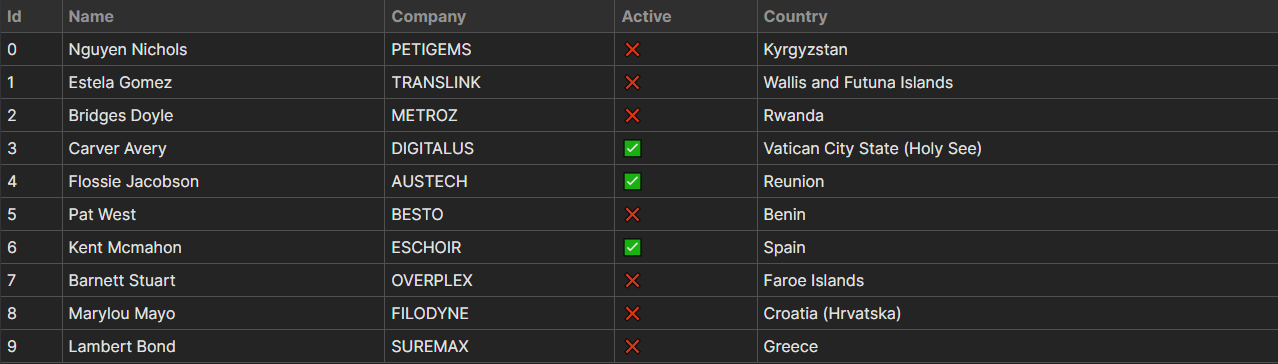
With the whole lot up to now, we’ve the next habits for the part.
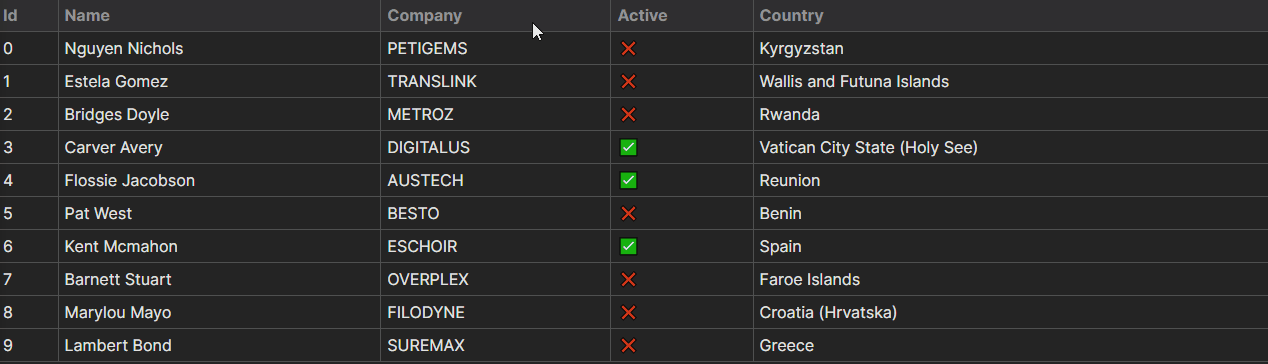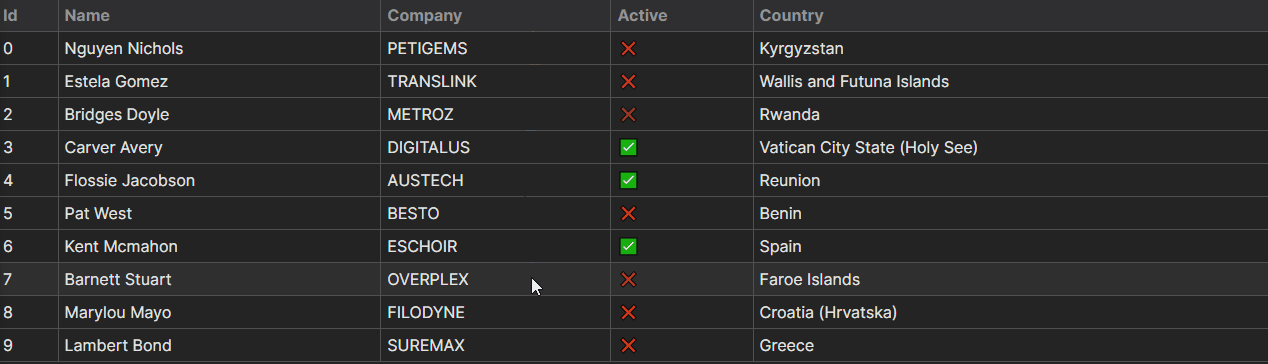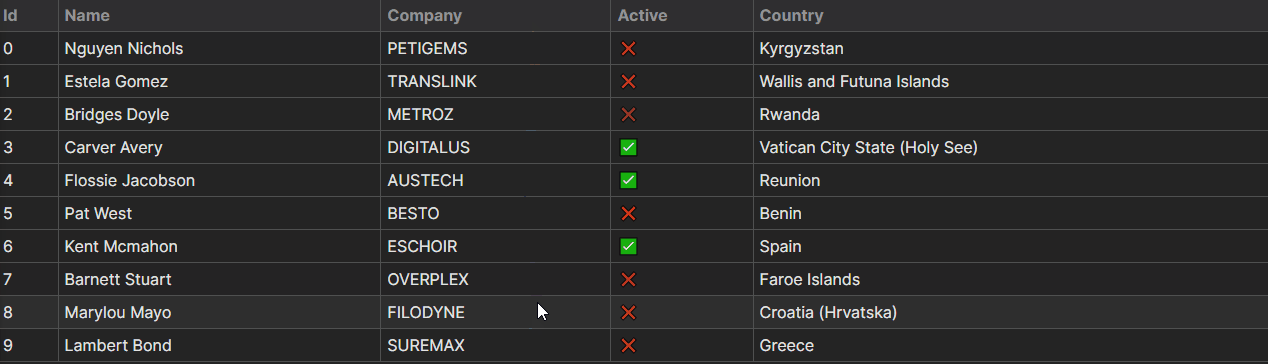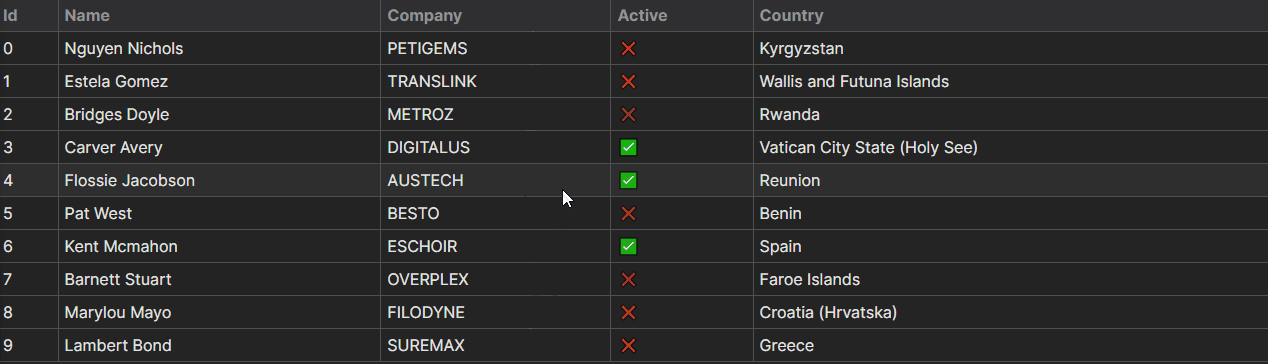
Including Controls
Now that we’ve styled the desk, let’s upload the controls for the kind and clear out capability. We’ll create an <enter> for the clear out and a <make a choice> component for the kind. We’ll additionally come with a button for switching between type orders (ascending/descending).
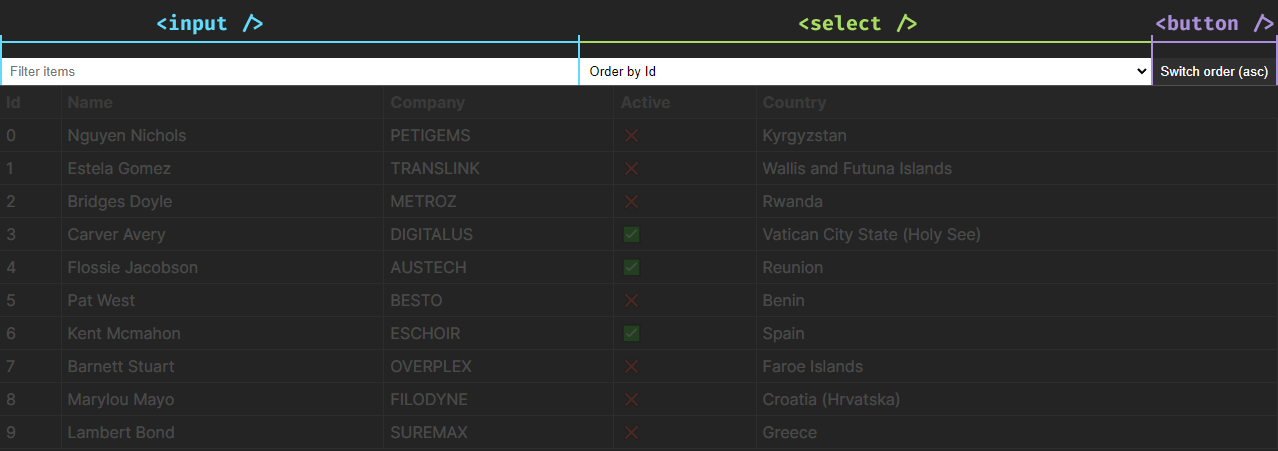
So as to add the inputs, we’ll additionally want new states for the present order (ascending or descending) and a variable to stay monitor of the kind key (which key within the object is used for sorting). With that during thoughts, lengthen the Desk part with the next:
const [order, setOrder] = useState('asc')
const [sortKey, setSortKey] = useState(Object.keys(rows[0])[0])
const clear out = (match: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {}
const type = (worth: keyof Information[0], order: string) => {}
const updateOrder = () => {}
go back (
<>
<div className="controls">
<enter
kind="textual content"
placeholder="Clear out pieces"
onChange={clear out}
/>
<make a choice onChange={(match) => type()}>
{Object.keys(rows[0]).map((access, index) => (
<possibility worth={access} key={index}>
Order by way of {capitalize(access)}
</possibility>
))}
</make a choice>
<button onClick={updateOrder}>Transfer order ({order})</button>
</div>
<desk>...</desk>
</>
)
Let’s move so as to perceive what modified:
order. First, we wish to create a brand new state for the kind order. This may also be one amongascordesc. We’ll use its worth within thetypeserve as.sortKey. We additionally desire a state for the kind key. By means of default, we will grasp the important thing of the first actual assets in our array of items the use ofObject.keys(rows[0])[0]. We’ll use this to stay monitor of the kind when switching between orders.clear out. We’ll desire a serve as for filtering effects. This must be handed to theonChangematch at the<enter>component. Observe thatReact.ChangeEventis a generic and will settle for the kind of HTML component that brought about the exchange.type. Identical to theclear outserve as, this may occasionally wish to be hooked up to theonChangematch, however this time, at the<make a choice>component. It is going to settle for two parameters:
worth. It will possibly take keys of our knowledge object. We will specify the sort the use of thekeyofkey phrase. It signifies thatworthmay also be one amongidentity,identify,corporate,energetic, ornation.order. The order of the kind, bothascordesc.
updateOrder. Finally, we additionally desire a serve as for updating the order. This can be brought about on button click on.Observe that we use the similar common sense we did for the <th> components for dynamically producing the choices for the <make a choice>. We will additionally reuse the capitalize software serve as to structure the choices.

Styling controls
Let’s taste the controls ahead of shifting ahead. This may also be executed with only a handful of CSS regulations. Lengthen desk.css with the next:
.controls {
show: flex;
}
enter,
make a choice {
flex: 1;
padding: 5px 10px;
border: 0;
}
button {
background: #2f2f2f;
colour: #FFF;
border: 0;
cursor: pointer;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
This may occasionally make sure that inputs are aligned subsequent to one another. By means of the use of flex: 1 at the <enter> and <make a choice> components, we will lead them to absorb an equivalent quantity of width from the to be had area. The <button> will absorb as a lot area as wanted for its textual content.
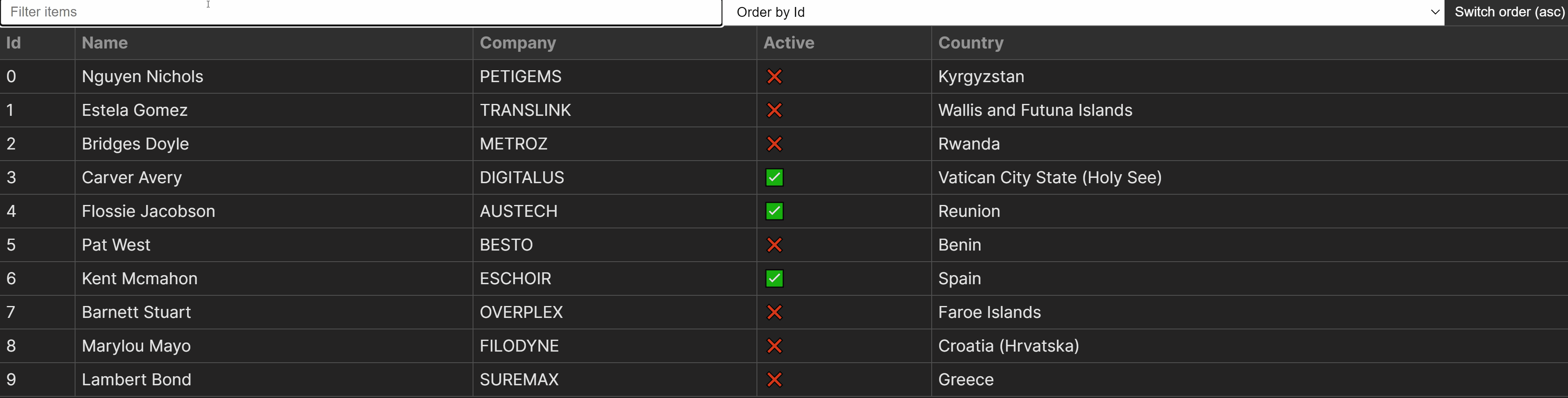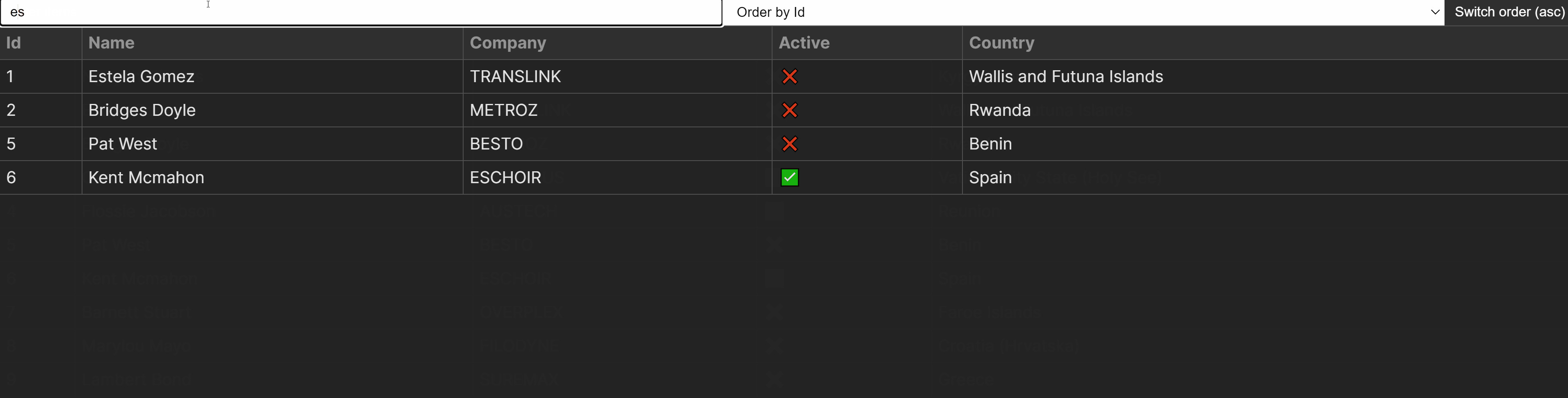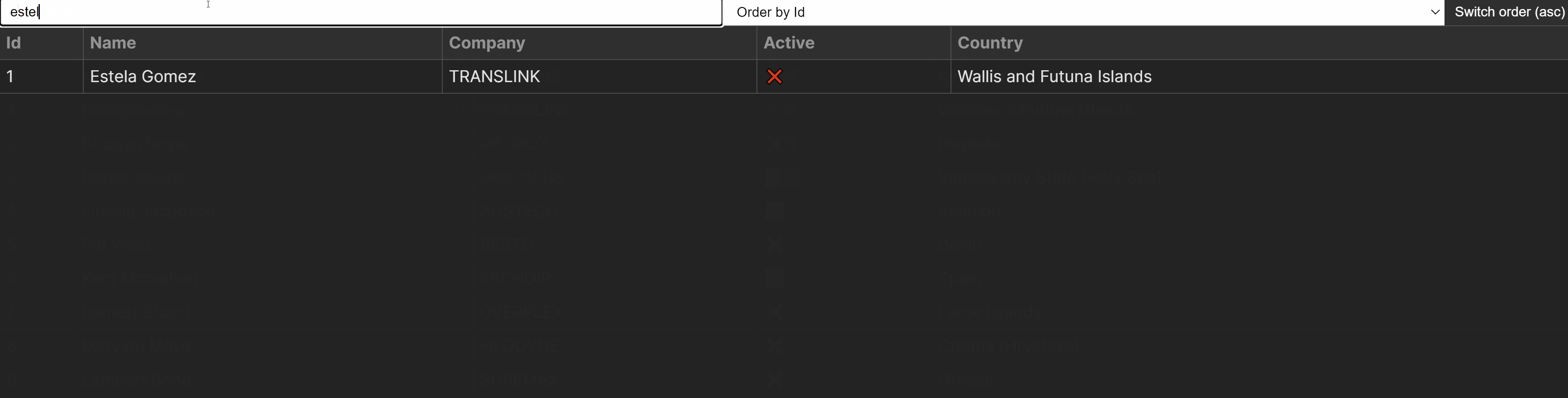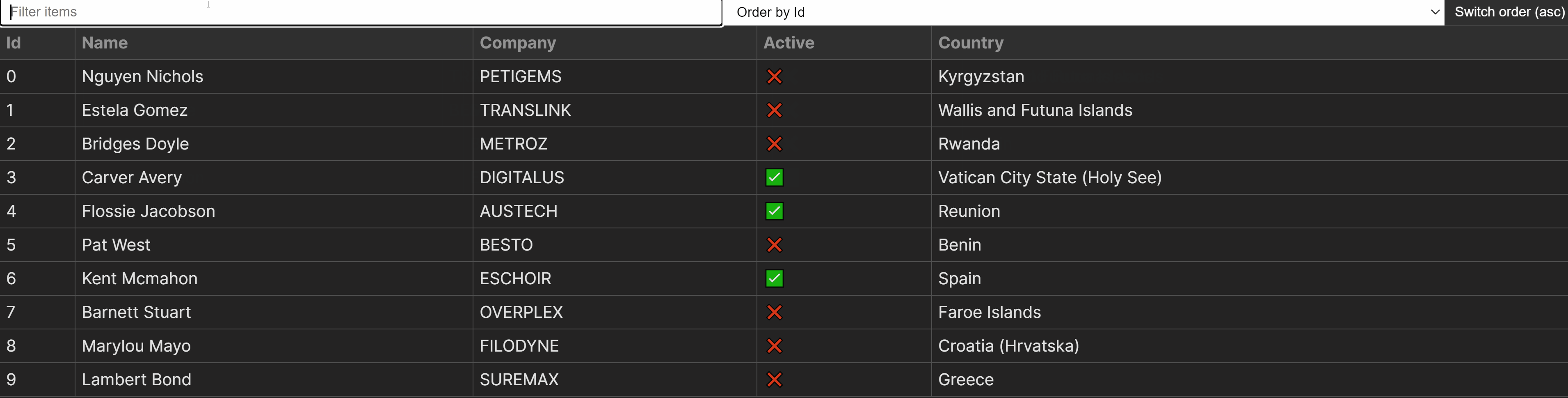
Filtering the Desk
Now that we’ve got the controls in position, let’s take a look at imposing the capability. For filtering the desk in accordance with any box, we’ll wish to observe this common sense:
const rows = [
{
id: 0,
name: 'Jaime Wallace'
},
{ ... }
]
setRows([ ...rows ].clear out(row => { ... }))
Object.values(row) -> [0, 'Jaime Wallace']
[0, 'Jaime Wallace'].sign up for('') -> '0Jaime Wallace'
'0Jaime Wallace'.toLowerCase() -> '0jaime wallace'
'0jaime wallace'.comprises(worth) -> true / false
With the whole lot mixed, we will create the go back worth for the clear out in accordance with the above common sense. This leaves us with the next implementation for the clear out serve as:
const clear out = (match: React.ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
const worth = match.goal.worth
if (worth) {
setRows([ ...rows.filter(row => {
return Object.values(row)
.join('')
.toLowerCase()
.includes(value)
}) ])
} else {
setRows(rows)
}
}
Observe that we additionally need to take a look at if the worth is provide. Its absence method the <enter> box is empty. In such instances, we need to reset the state and cross the unfiltered rows to setRows to reset the desk.

Sorting the Desk
We now have the clear out capability, however we’re nonetheless lacking sorting. For sorting, we now have two separate purposes:
type. The serve as that may care for sorting.updateOder. The serve as that may transfer the order of sorting from ascending to descending and vice versa.
Let’s get started with the kind serve as first. On every occasion the <make a choice> adjustments, the type serve as can be known as. We need to use the worth of the <make a choice> component to come to a decision which key to make use of for sorting. For this, we will use a easy type manner and bracket notation to dynamically evaluate object keys:
const type = (worth: keyof Information[0], order: string) => {
const returnValue = order === 'desc' ? 1 : -1
setSortKey(worth)
setRows([ ...sortedRows.sort((a, b) => {
return a[value] > b[value]
? returnValue * -1
: returnValue
}) ])
}
Let’s move in the course of the serve as from best to backside to higher perceive the implementation.
returnValue. In keeping with theorderstate, we would like the go back worth to be both 1 or -1. This is helping us outline the kind order (1 for descending and -1 for ascending).setSortKey. Theworthhanded to the serve as is the worth of the<make a choice>component. We need to report this worth in our state (sortKey), which we will do by way of calling thesetSortKeyupdater serve as.setRows. The real sorting occurs on this name. The use of bracket notation, we will evaluatea[value]withb[value]and go back both -1 or 1.
Let’s take the next for example:
const rows = [{ id: 0 }, { id: 1 }]
const worth = 'identity'
rows.type((a, b) => a[value] > b[value] ? -1 : 1)
rows.type((a, b) => a[value] > b[value] ? 1 : -1)
Switching between type orders
To replace the kind order, we simply wish to replace the order state each time the button is clicked. We will do so with the next capability:
const updateOrder = () => {
const updatedOrder = order === 'asc' ? 'desc' : 'asc'
setOrder(updatedOrder)
type(sortKey as keyof Information[0], updatedOrder)
}
It’ll set the order to its reverse on every click on. Observe that when we replace the order state the use of setOrder, we additionally wish to name the type serve as to hotel the desk in accordance with the up to date order. To deduce the right kind kind for the sortKey variable, we will reference the keys of the Information kind the use of typecasting: as keyof Information[0]. As the second one parameter, we additionally wish to cross the up to date order.
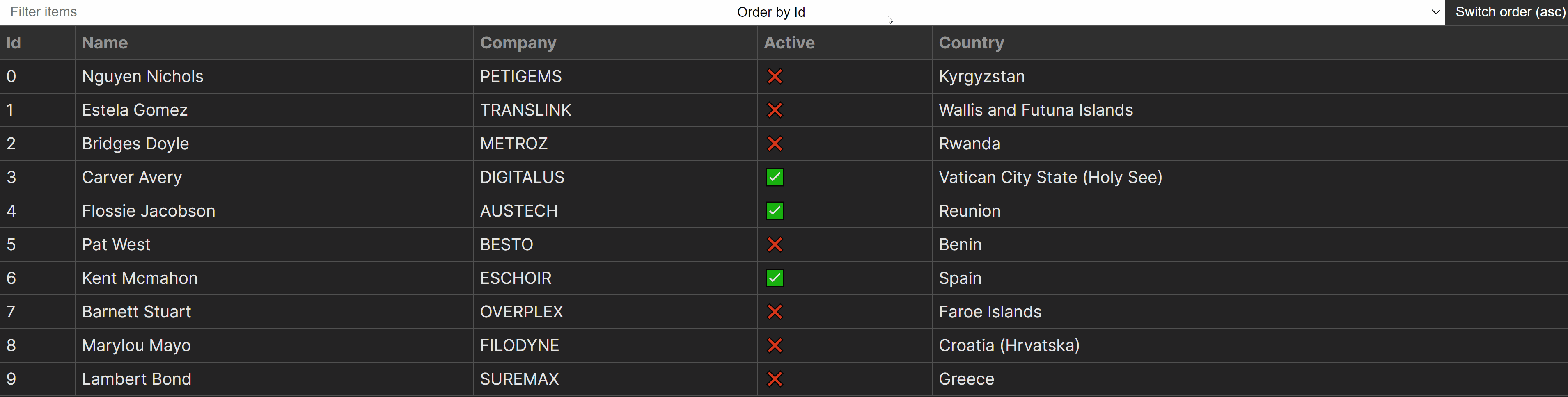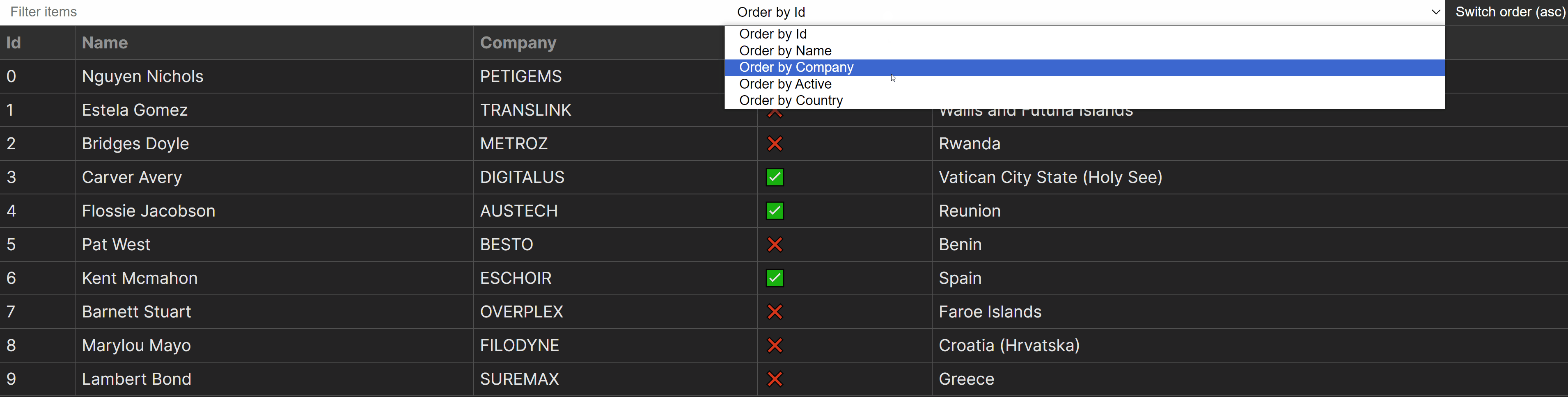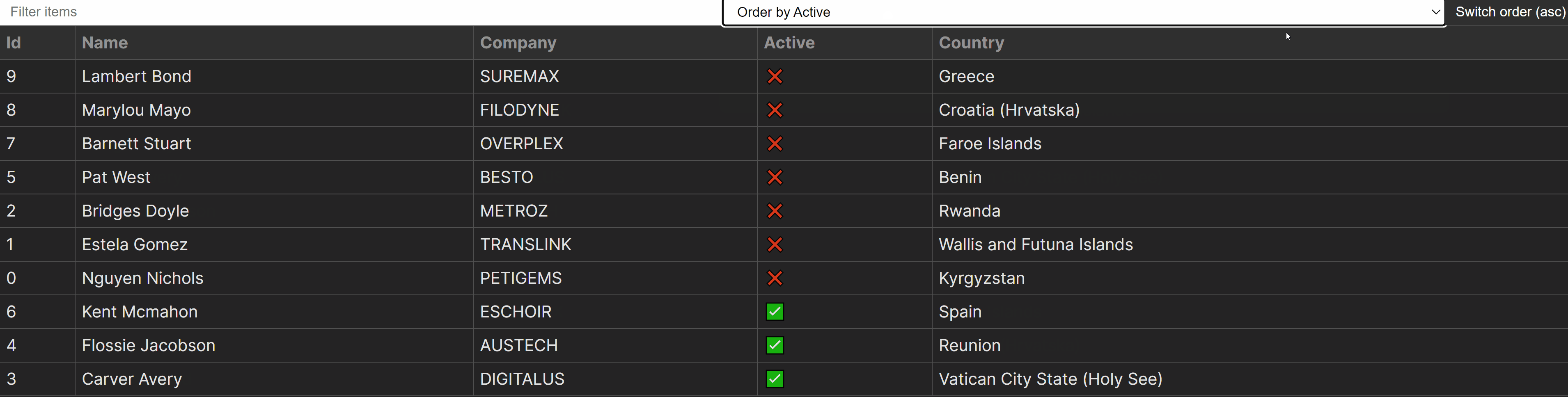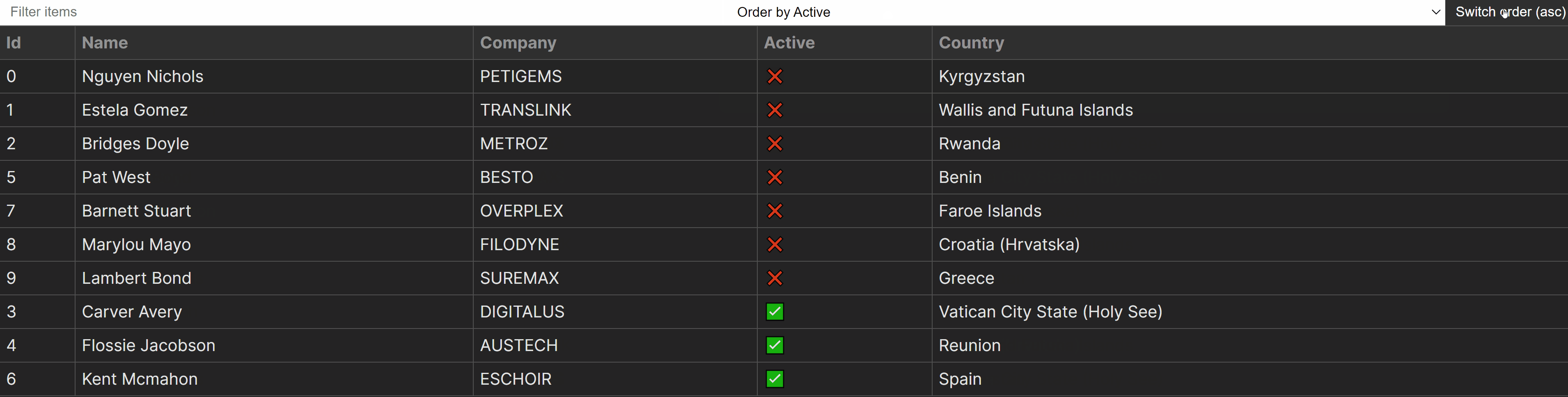
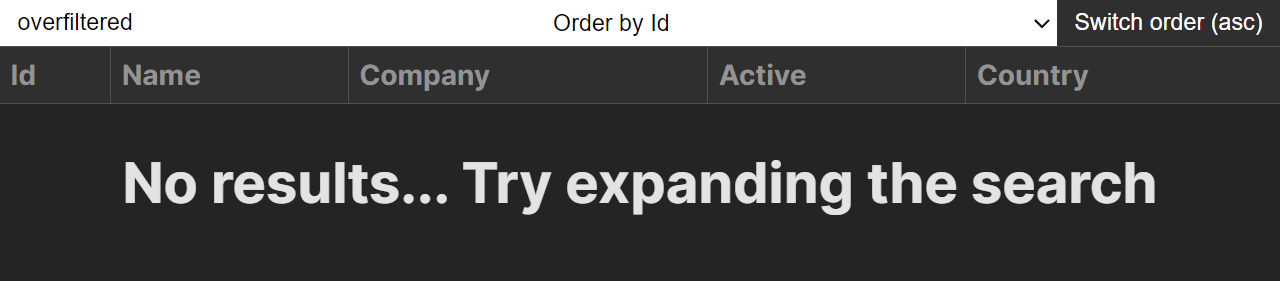
Dealing with Overfiltering
To finish this venture, let’s upload some indication for an overfiltered state. We simplest need to display an overfiltered state if there aren’t any effects. This may also be simply executed by way of checking the duration of our sortedRows state. After the <desk> component, upload the next:
go back (
<>
<div className="controls">...</div>
<desk>...</desk>
{!sortedRows.duration && (
<h1>No effects... Take a look at increasing the hunt</h1>
)}
</>
)
Conclusion
In conclusion, development a sortable and filterable desk in React doesn’t should be sophisticated. With array strategies and serve as chaining, the use of the correct capability, we will create concise and exact purposes for dealing with those duties. With the whole lot incorporated, we controlled to suit all the common sense into lower than 100 traces of code.
As observed at first of this educational, all the venture is to be had in a single piece on GitHub. Thanks for studying via; glad coding!
[ad_2]