[ad_1]
HTTP GET requests will have to all the time be secure to execute as a result of they’re supposed to learn the state of the gadget in an idempotent type. Different HTTP strategies (verbs)—equivalent to POST and DELETE—that are supposed to mutate the state of the gadget, can also be unhealthy and will have to be validated. That means, you by no means need to permit a GET request to invoke a useful resource that deserves a POST manner. I sought after to take a handy guide a rough have a look at how you’ll put in force the HTTP request manner in ColdFusion.
The best way to put in force the HTTP manner in ColdFusion is to take action implicitly via depending at the URL and FORM scopes to ship the other units of information. By means of default, the URL scope most effective incorporates the information provide within the request URL. And, the FORM scope most effective incorporates the information found in a sort submission.
This means that, if you wish to have to make sure that a request is processed as a part of a sort submission, take a look at the shape scope—and most effective the shape scope—for that information.
To look what I imply, let us take a look at a easy ColdFusion web page that incorporates each a <shape> component and an <a> component which seeks to impersonate the shape:
<cfscript>
// On this model, the SUBMITTED price is most effective seen within the FORM scope, which
// signifies that we will be assured that the request was once submitted by means of an HTTP POST (if
// the worth is correct).
param identify="shape.submitted" sort="boolean" default=false;
if ( shape.submitted ) {
// ... processing shape, mutating the gadget state...
}
</cfscript>
<cfoutput>
<cfif shape.submitted>
<p>
<mark>Thanks on your submission</mark>!
</p>
</cfif>
<!--- REAL shape submission. --->
<shape manner="put up" motion="take a look at.cfm">
<enter sort="hidden" identify="submitted" price="true" />
<button sort="post">
Publish Shape
</button>
</shape>
<!--- FAKE (probably malicious) shape submission. --->
<p>
<a href="https://www.bennadel.com/weblog/take a look at.cfm?submitted=true">Pretend Publish</a>
</p>
</cfoutput>
As you’ll see, each the <shape> and the <a> are making an attempt to “post” to the URL, take a look at.cfm?submitted=true; however, once we move to procedure the request, we’re most effective taking a look on the shape scope for the submitted flag. As such, we’re implicitly checking out the HTTP manner:
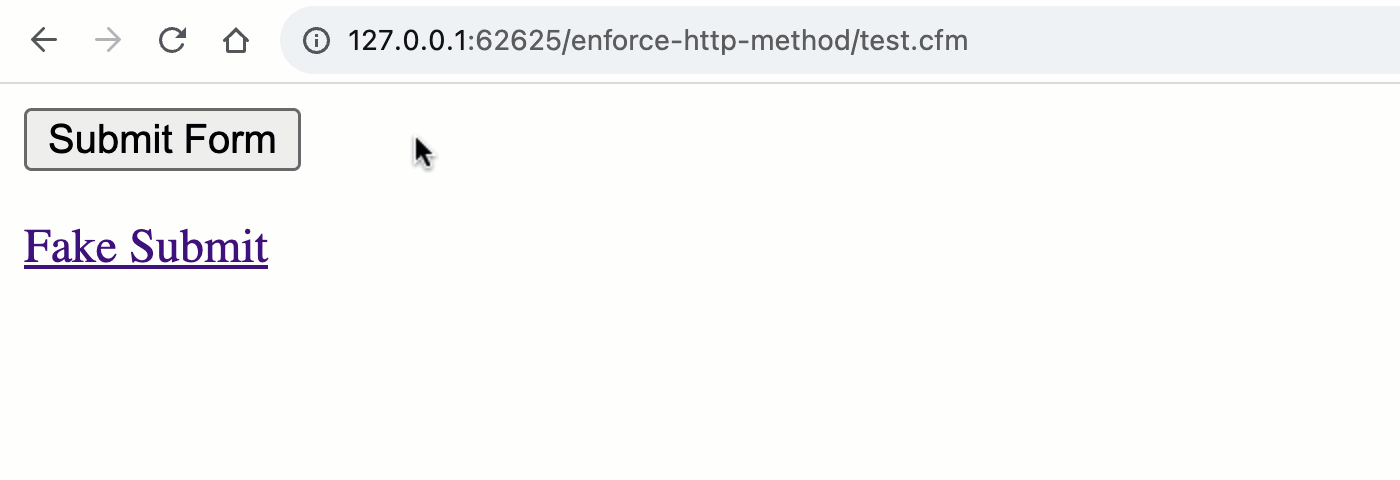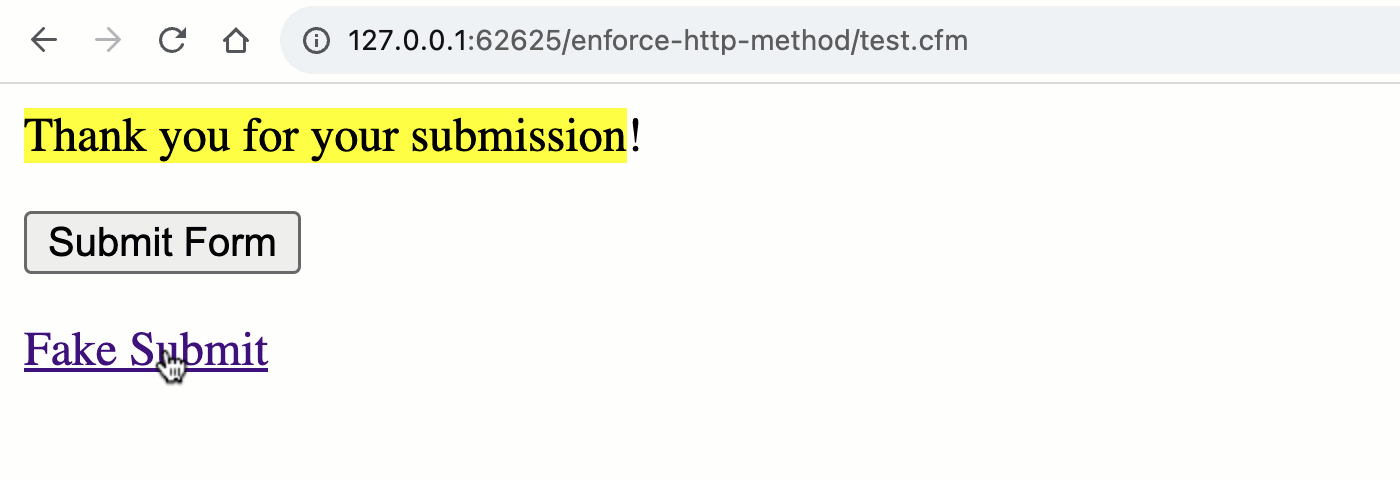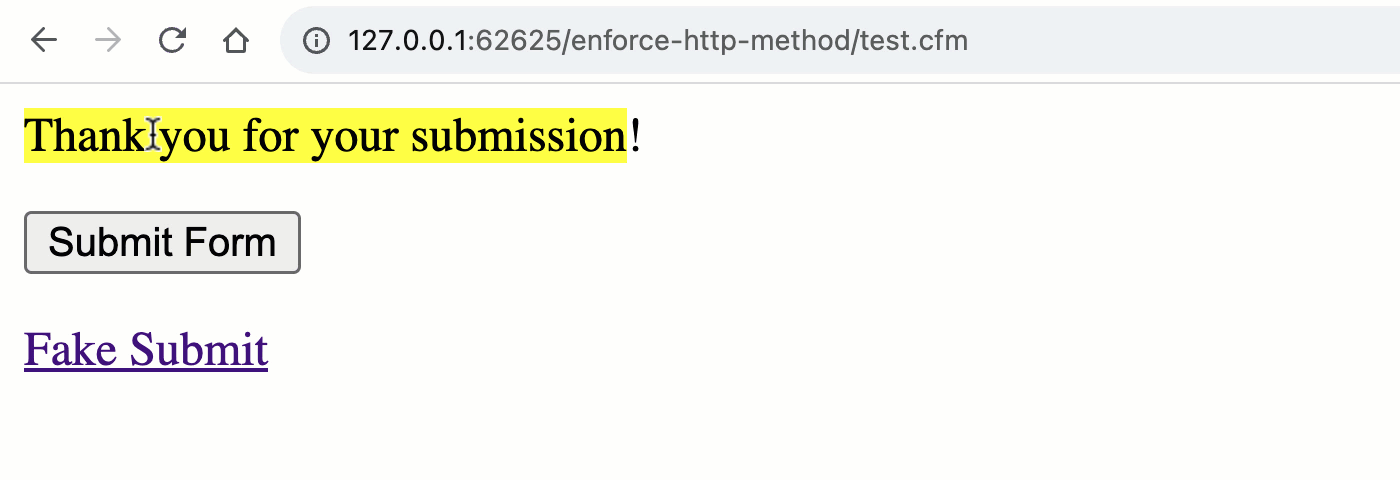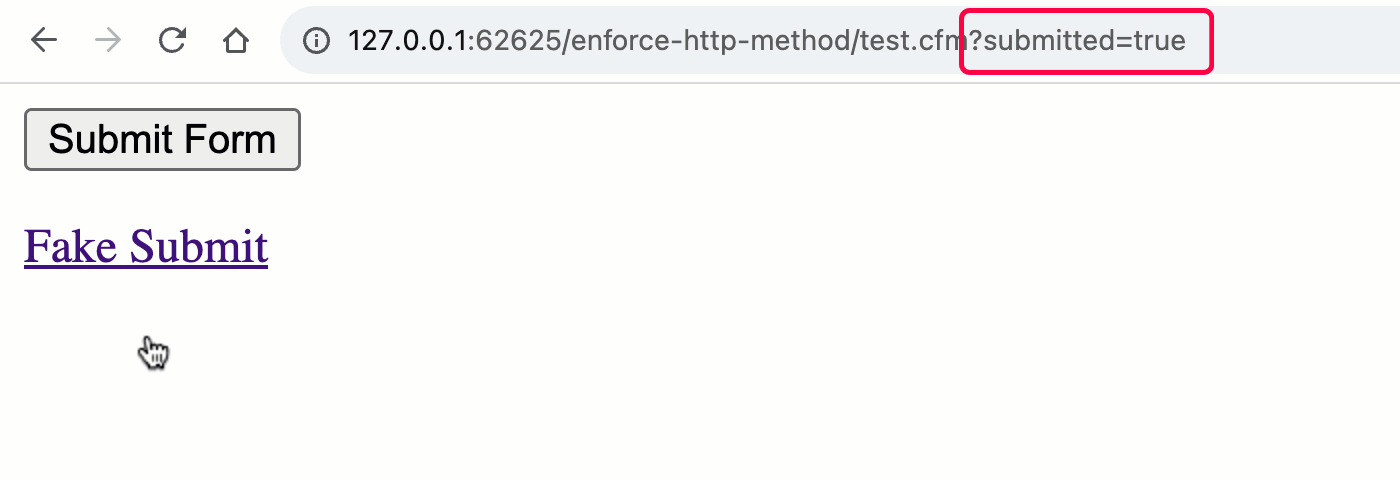
Word that the “Thanks” message is most effective rendered all the way through a POST request and no longer all the way through the GET request. By means of the usage of the best ColdFusion scope, we’ve got implicitly validated the request manner.
In most of the ColdFusion internet frameworks, alternatively, the URL and FORM scopes are blended right into a unmarried “request context”. So, as an alternative of explicitly referencing the URL and FORM scopes, you depend on a generated scope, equivalent to rc (for “request context”).
Since this rc scope is populated via each the URL and FORM scopes, it signifies that “put up” information can simply be equipped via a “get” request. What follows is similar ColdFusion code as above, most effective we are changing shape. with rc.:
<cfscript>
// Mocking out a commonplace framework manner by which the FORM and URL scopes are
// blended right into a unmarried "request context" scope.
rc = structNew()
.append( url )
.append( shape )
;
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- //
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- //
// On this model, the SUBMITTED price is seen within the RC scope, because of this that
// it may possibly equipped both throughout the URL or the FORM scope. As such, we CANNOT be
// assured in regards to the present HTTP manner.
param identify="rc.submitted" sort="boolean" default=false;
if ( rc.submitted ) {
// ... processing shape, mutating the gadget state...
}
</cfscript>
<cfoutput>
<cfif rc.submitted>
<p>
<mark>Thanks on your submission</mark>!
</p>
</cfif>
<!--- REAL shape submission. --->
<shape manner="put up" motion="test2.cfm">
<enter sort="hidden" identify="submitted" price="true" />
<button sort="post">
Publish Shape
</button>
</shape>
<!--- FAKE (probably malicious) shape submission. --->
<p>
<a href="https://www.bennadel.com/weblog/test2.cfm?submitted=true">Pretend Publish</a>
</p>
</cfoutput>
Now that the rc scope is pulling information from each the URL and FORM scopes, each strategies can cause a “shape submission”:

As you’ll see, once we transfer to the unified rc scope, we now not get the implicit validation of the HTTP manner. This means that, each the GET and POST requests can cause the “shape processing” workflow.
At this level, we need to transfer from an implicit validation to an particular validation. This means that, in reality saying that the incoming request is the usage of the predicted HTTP manner / verb. And, for that, we will have a look at the CGI scope, which incorporates the present request manner:
<cfscript>
// Mocking out a commonplace framework manner by which the FORM and URL scopes are
// blended right into a unmarried "request context" scope.
rc = structNew()
.append( url )
.append( shape )
;
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- //
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- //
// On this model, the SUBMITTED price is seen within the RC scope, because of this that
// it may possibly equipped both throughout the URL or the FORM scope. As such, we CANNOT be
// assured in regards to the present HTTP manner.
param identify="rc.submitted" sort="boolean" default=false;
if ( rc.submitted ) {
// For the reason that SUBMITTED price may well be coming via by means of a MALICIOUS GET, we want
// to validate / assert that the request manner is a POST. Since any non-POST is
// regarded as malicious on this context, we do not want to "get well gracefully" -
// protective the gadget is the concern, the consumer revel in (UX) isn't.
assertHttpMethod( "POST" );
// ... processing shape, mutating the gadget state...
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- //
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- //
/**
* I assert that the present HTTP request is the usage of the given manner. If this is the case, this
* serve as quietly returns; if no longer, an error is thrown so as to offer protection to the gadget.
*/
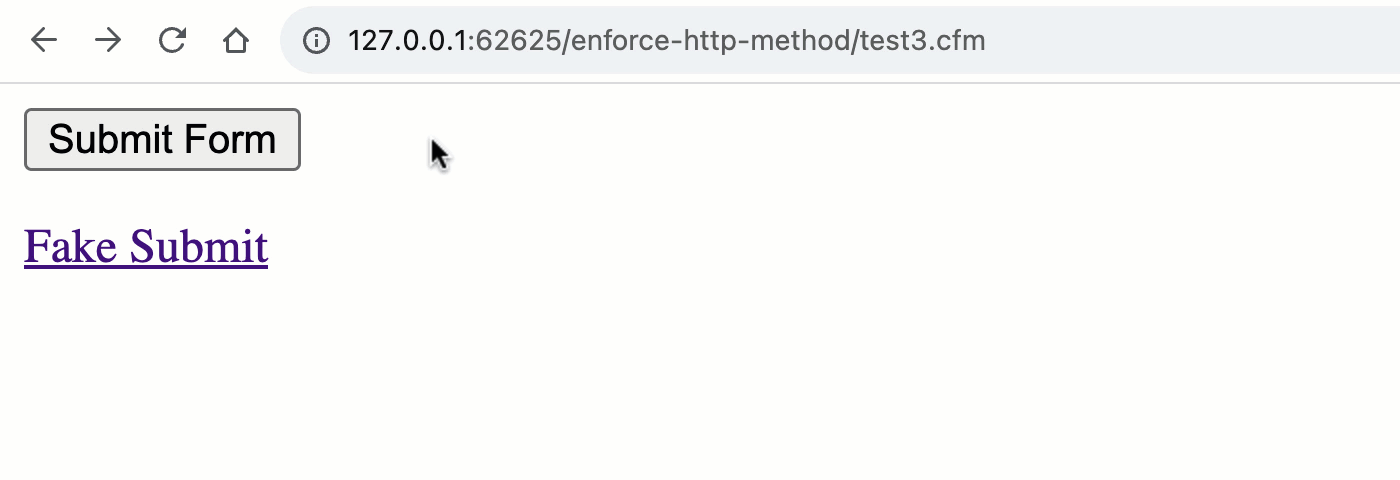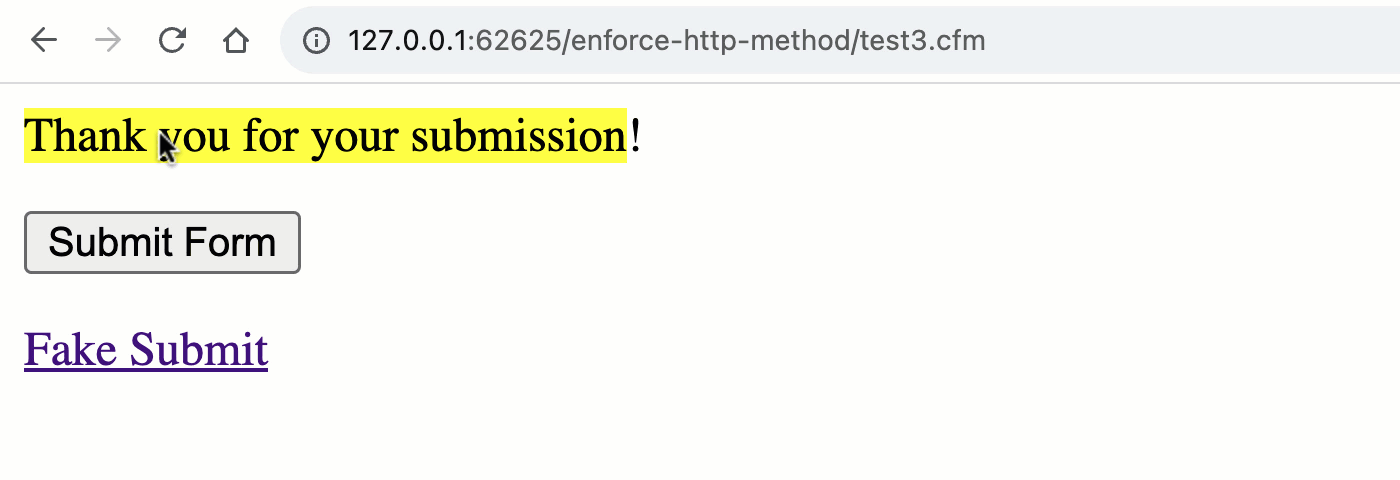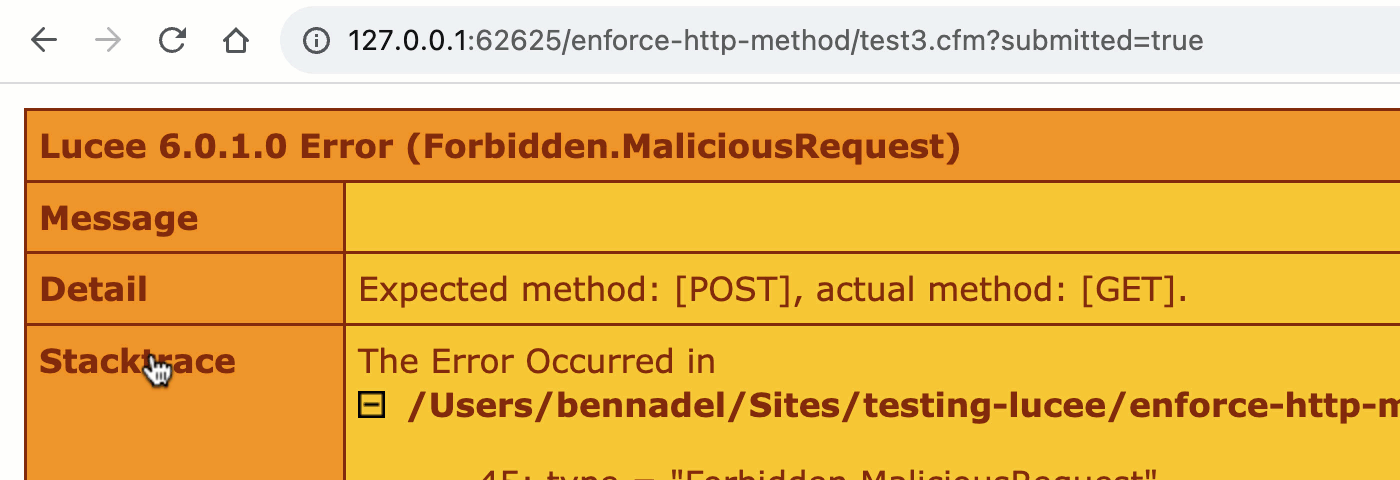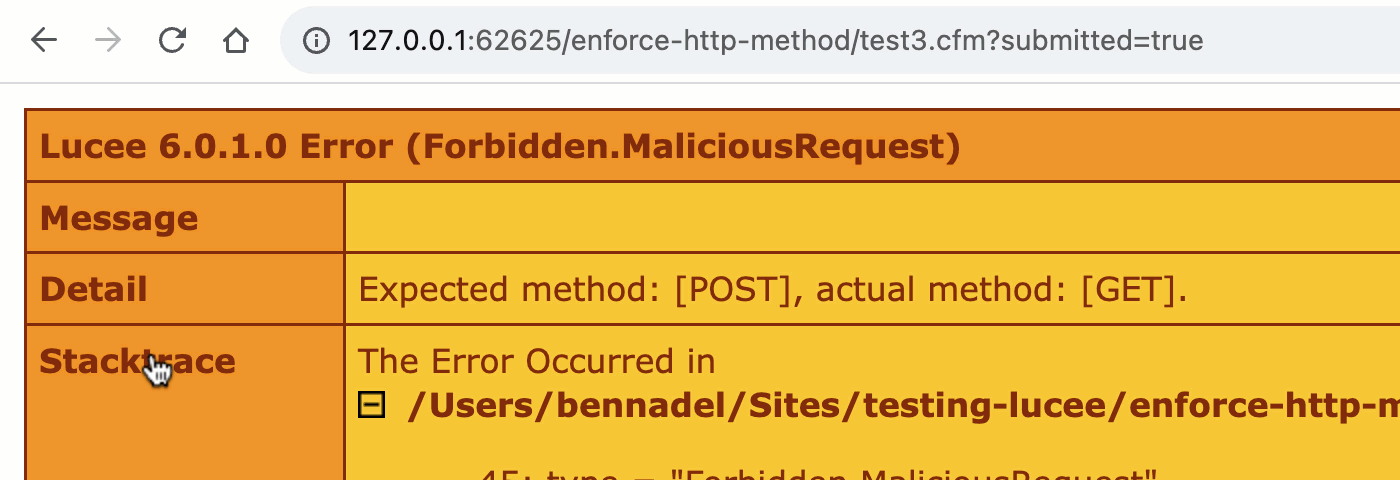
public void serve as assertHttpMethod( required string manner ) {
if ( cgi.request_method == manner ) {
go back;
}
throw(
sort = "Forbidden.MaliciousRequest",
manner = "Invalid HTTP manner utilized in request.",
element = "Anticipated manner: [#method#], exact manner: [#cgi.request_method#]."
);
}
</cfscript>
<cfoutput>
<cfif rc.submitted>
<p>
<mark>Thanks on your submission</mark>!
</p>
</cfif>
<!--- REAL shape submission. --->
<shape manner="put up" motion="test3.cfm">
<enter sort="hidden" identify="submitted" price="true" />
<button sort="post">
Publish Shape
</button>
</shape>
<!--- FAKE (probably malicious) shape submission. --->
<p>
<a href="https://www.bennadel.com/weblog/test3.cfm?submitted=true">Pretend Publish</a>
</p>
</cfoutput>
As you’ll see, this time, within the shape processing block, we read about the cgi.request_method and make certain that it in reality incorporates the HTTP manner that we want. And, if it does not, we throw an error and halt the present request processing regulate glide:
The express take a look at is extra verbose; however, it is also extra versatile. Once we implicitly validate the request by means of the URL and FORM scopes, we will truly most effective differentiate between the GET and POST strategies. On the other hand, once we upload an particular HTTP request manner take a look at, we will begin to differentiate between all the HTTP verbs (together with PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, HEAD, and many others).
Apart: Throwing an error may appear a bit of heavy-handed. However, needless to say we are validating towards an sudden / malicious invocation. Convalescing “gracefully” is not important as this pathway is not one thing a typical consumer will have to ever revel in.
An Eye on Safety
It is value temporarily discussing why it’s (or, can also be) unhealthy to permit GET routing to invoke state mutation. Whilst POST and DELETE requests normally contain the consumer explicitly beginning an motion, GET requests can also be prompted “at the sly” the usage of one thing like an <img> supply. Unvalidated HTTP strategies permit a “unhealthy actor” to craft GET requests for an unsuspecting sufferer:
<img src="https://www.bennadel.com/some/malicious/request" />
Whilst this src characteristic won’t level to a legitimate symbol, it would possibly not subject – the browser will nonetheless make the GET request on behalf of the sufferer. And, if the objective server lets in this GET request to mutate the gadget, the “unhealthy actor” will be capable of make malicious requests to the gadget via proxy.
Imposing the HTTP manner is not a solve-all; however, it’s one phase in a multi-prong safety effort. One-time use shape tokens, XSRF (Move-Web site Request Forgery) tokens, Content material Safety Coverage (CSP), and SameSite cookie settings are all further mechanics that may be added on best of the HTTP manner validation to lend a hand create a safe ColdFusion software.
Wish to use code from this put up?
Take a look at the license.
[ad_2]
